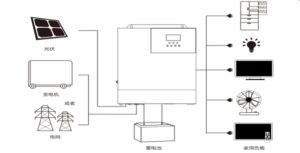
What is an inverter? Inverters convert direct current (DC, battery for short) into alternating current (AC, household appliances, directly connected to sockets for short). In most cases, the input DC voltage is usually low, while the output AC is equal to the voltage supplied by the power grid, that is, 120V, or 240V, depending on the country.
The inverter can be used as an independent device for solar power generation and other applications, or as a backup power supply for separately charged batteries. Another configuration is when it is part of a larger circuit, such as a power supply unit, or UPS. When there is power, it comes from the rectified AC power in the UPS, and when there is power failure, it comes from the battery.
The inverter used in photovoltaic products also has the maximum power tracking MPPT. By adjusting the DC voltage and output current, the module can always work at the maximum working point and output the maximum power under the current temperature and sunlight conditions. Because the input power of the PV module changes nonlinearly when the sunshine intensity and ambient temperature change, the PV module is neither a constant voltage source nor a constant current source, and its power changes with the output voltage, regardless of the load.
In addition, some inverters have the bidirectional inverter function, not only DC to AC, but also AC to DC. However, they are generally used above 2KW, because the cost of this function will be higher.
There are also many application scenarios of inverters, such as: solar buildings (BIPV), photovoltaic power stations, home lighting power supply, oil, ocean, weather, communication/communication, transportation, user solar power, etc.If you want to know more about solar panels, please contact us, the solar panel manufacturer – Huanqi Technology (Shenzhen) Co., Ltd.